In this article we will look at the step-by-step guide to deploy a chatbot application on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) using git and Docker.
Please note that this article does not discuss the development of the application. The application used as an example to explain deployment is a python based web chatbot application with a Streamlit based user interface.
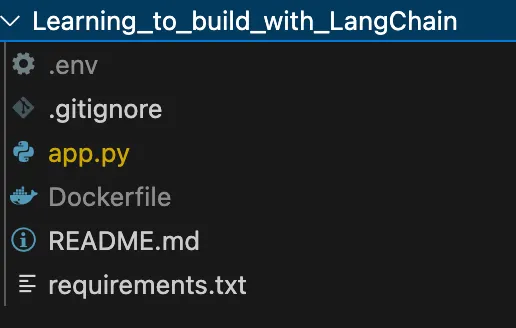
The general structure of my application:
Step 1: Containerize your Application with Docker
Containerising your application using Docker before deploying it on cloud offers several benefits such as:
- Portability — Docker packages the application and all its dependencies into a single unit which can then be run on any device making it easily accessible. This avoids any machine specific issues that might arise while trying to run on a different device or environment.
- Isolation and Security — Containerization helps isolate the application within from other containers and the host system. This protects the container from any security breach or potential dependency conflicts with other containers.
- Scalability — Containers make it easy to scale applications as and when required. With orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, scaling and other tasks can also be automated.
- Consistency across all devices — Containerisation helps avoid device or environment dependency. Packaging all the dependencies required to run the application in the container helps it run smoothly with minimal bugs if not none on any device by just using the container image. This is crucial especially when collaborating with a large number of developers and in different environments such as development, testing, staging, and production.
- Management and Automation — Docker images can be versioned, shared, and rolled back quickly. This supports modern DevOps practices, automated testing, and easy integration with cloud-native tools.
Install Docker
- Go to the Docker website and download Docker Desktop for Windows/macOS.
- For Linux, install Docker using the terminal:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg]
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioCreate a Dockerfile
- In your project directory, create a file named ‘Dockerfile’.
- Add instructions to build your Docker image. For example, my app is a python streamlit app.
# Use an official Python runtime as a parent image
FROM python:3.9-slim
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the requirements file
COPY requirements.txt .
# Install any needed packages specified in requirements.txt
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy the application code
COPY . .
# Make port 8501 available to the world outside this container
EXPOSE 8080
# Run app.py when the container launches
CMD ["streamlit", "run", "app.py", "--server.port=8080"]Build the Docker Image
Run the following command in your terminal:
docker build -t myapp .- docker build : This command tells Docker to build an image from the instructions in the Dockerfile.
- -t myapp : The -t flag stands for “tag.” It specifies the name you want to give your Docker image. In this case, myapp is the tag or name of the image.
- . : The dot at the end of the command tells Docker to look for the Dockerfile in the current directory.
- When you run this command, Docker reads the instructions from the Dockerfile in your current directory and builds an image with the name ‘myapp’. This image can then be used to create containers.
Step 2: Deploy on Google Cloud Using Free Credits
Create a Google Cloud Account
- Go to cloud.google.com and create an account if you haven’t already.
- You’ll receive $200 in free credits valid for 90 days.
Enable Billing
- Ensure billing is enabled for your project to use free credits.
Install Google Cloud CLI
- Follow the instructions on the Google Cloud website to install the gcloud CLI.
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
Run `gcloud init` to initialize the CLI and authenticate with your Google account.
Create a New Project
- Log in to the Google Cloud Console.
- Click on the Select a project dropdown and click New Project.
- Enter a project name and click Create.
Enable Artifact Registry API
- Search for “Artifact Registry” in the console and enable it.
- In the Google Cloud Console, navigate to APIs & Services > Dashboard.
- Search for “Artifact Registry API” and click Enable.
Tag and Push Your Docker Image
- Tag your Docker image with the Artifact Registry URL:
docker tag myapp us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/[PROJECT_ID]/[REPOSITORY_NAME]/my-chatbotPush the image to Artifact Registry:
docker push us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/[PROJECT_ID]/[REPOSITORY_NAME]/myappDeploy to Cloud Run
- Use the following command to deploy your image to Cloud Run
gcloud run deploy myapp-service --image us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/[PROJECT_ID]/[REPOSITORY_NAME]/myapp --region us-central1 --allow-unauthenticated- Replace [PROJECT_ID], [REPOSITORY_NAME], and my-chatbot-service with your actual project ID, repository name, and desired service name.
Once the deployment is complete you will see the URL of your deployed service.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully navigated the entire process of transforming your chatbot application from a local development environment to a production-ready deployment on Google Cloud Platform. By following this step-by-step approach, you’ve not only learned the technical aspects of containerization but also experienced firsthand why Docker has become such an essential tool in modern application deployment.
The combination of Docker’s containerization power and Google Cloud Platform’s robust infrastructure has given your chatbot application the wings it needs to soar. Now it’s time to see where this newfound capability takes your next project!