The evolution of AI has brought us 2 distinct types of language models:
- Traditional Large Language Models
- Chat-Based Models
While both are built on similar foundational technologies, their design, interaction patterns, and use cases differ significantly. This article explains these differences and highlights their strengths and limitations.
Traditional Large Language Models
A typical interaction with a traditional LLM will look like given below:
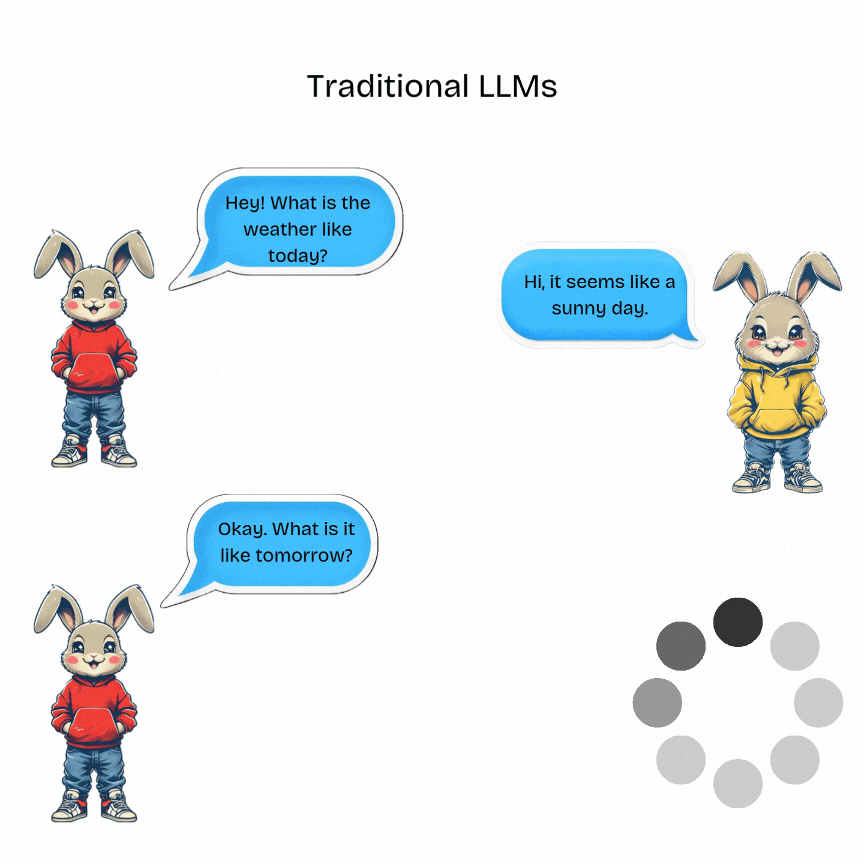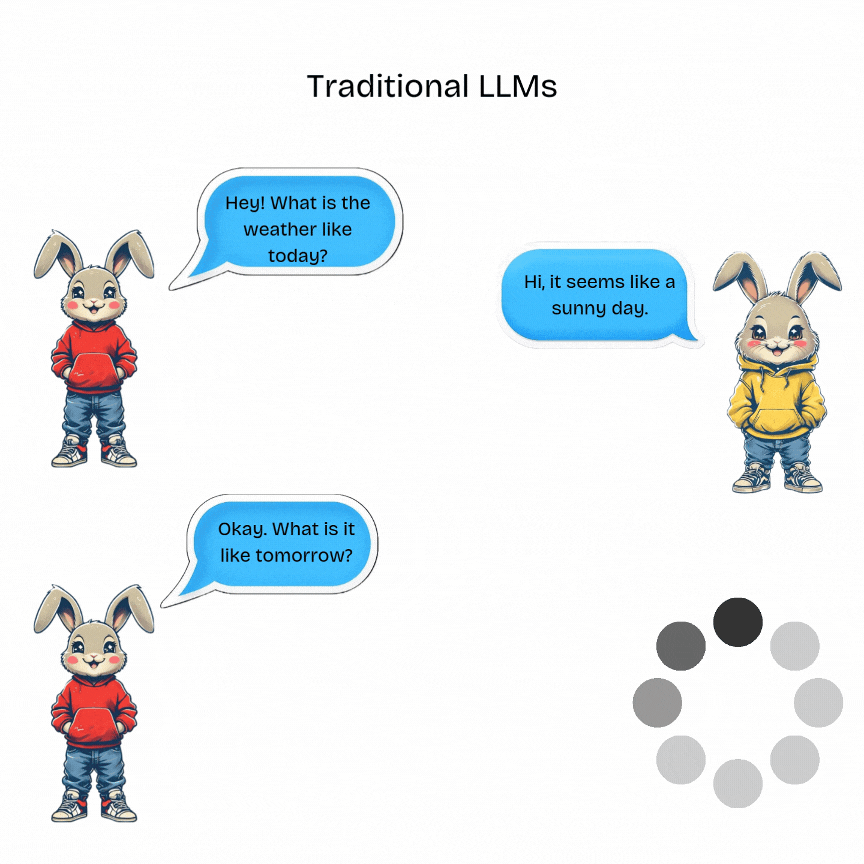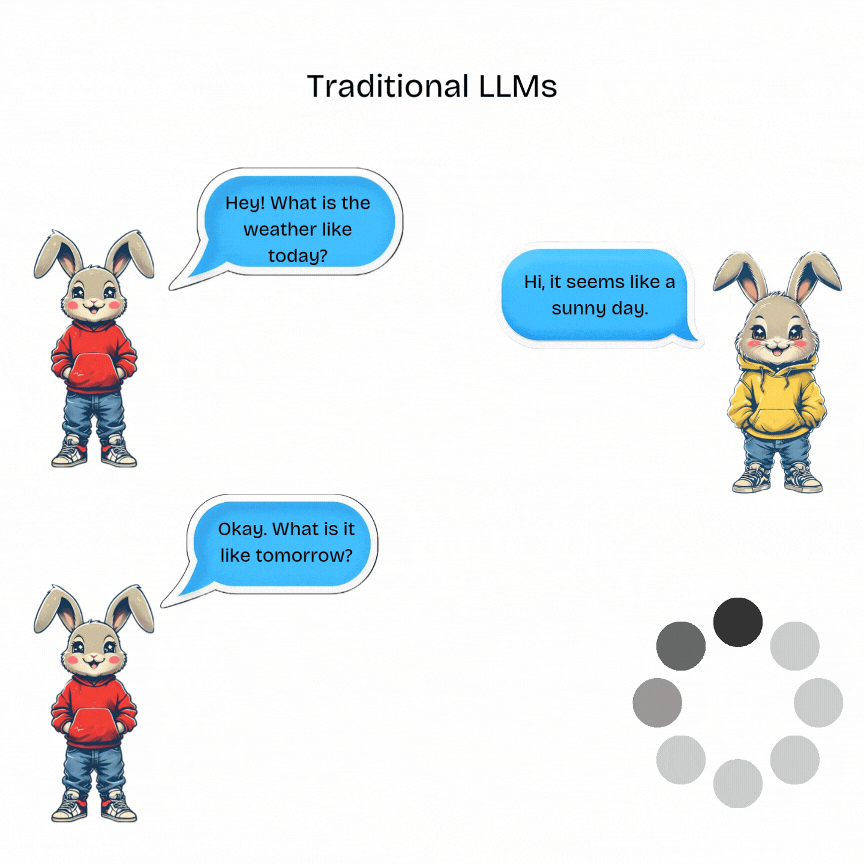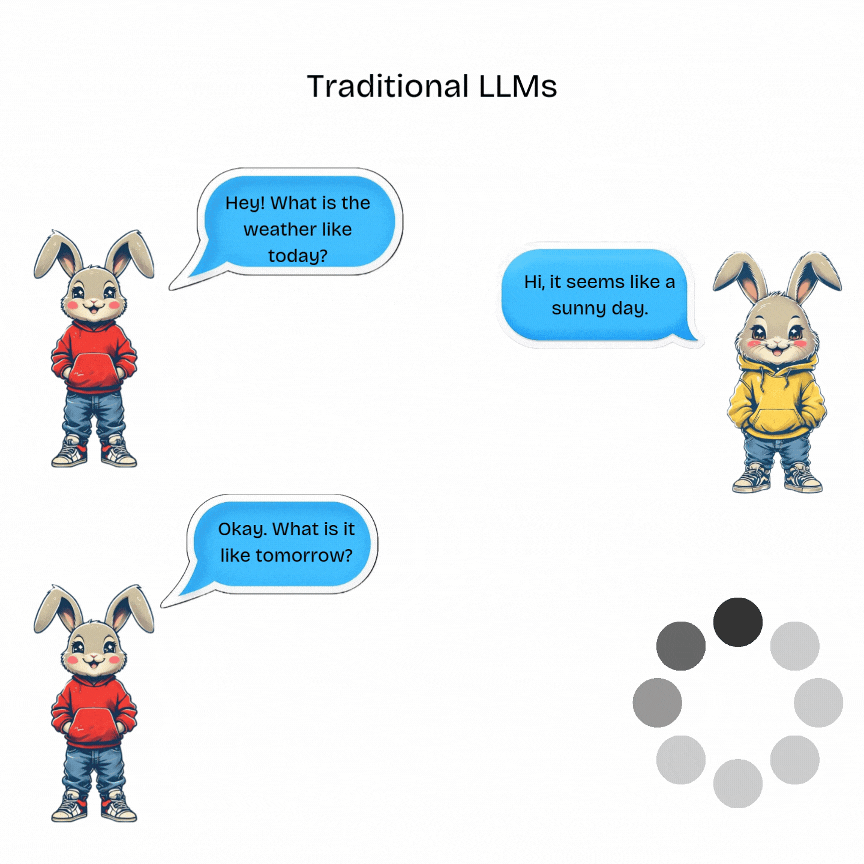
Traditional LLMs are designed for single-turn tasks. They have no memory of past interactions. They process a single input prompt and generate a corresponding output without retaining any conversational context.
Example Model: GPT-3, BloombergGPT, BERT, Llama 2 etc.
Some use cases of Traditional LLMs are: Text summarisation, Content generation, Translation etc.
Chat-Based Models
A typical interaction with a chat-based model will look like given below:
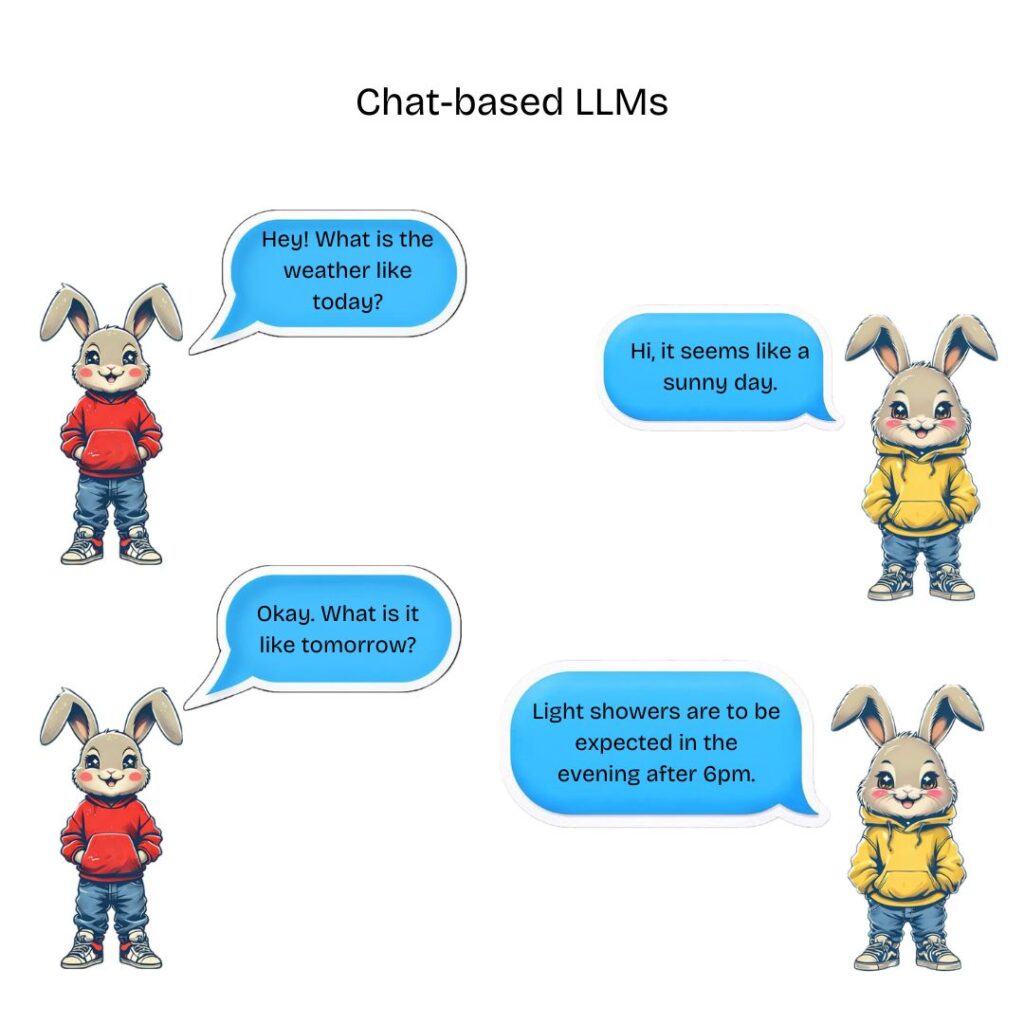

Chat-based models are designed for dynamic, multi-turn interactions. They excel at maintaining conversational context, making them ideal for dialogue-heavy applications. They retain contexts within conversations to provide personalised outputs for the user.
Example Model: GPT-4, Claude 3, Google Gemini etc.
Some use cases of Chat-based Models are: Virtual assistants, Customer service chatbots, Real-time tutoring etc.